WhatsMRI
Press info about the ERC Consolidator project WhatsMRI - Elemental and Structural Composition underlying Brain MRI.
Outline
Myelin acts as the electrical insulation of neuronal fibers and is essential for motor, sensory, and cognitive functions and is composed of several lipids and proteins arranged in a specific geometry. However, myelin loss occurs regionally in inflammatory diseases like multiple sclerosis, myelitis, and optic neuritis, and it also serves as a biomarker of aging. Despite the availability of various MRI-based approaches for detecting myelin, there remains a significant gap in systematically validated knowledge regarding how myelin's lipids, proteins, and structural variations influence MRI signal generation. Furthermore, there is no gold standard for assessing the constituents of myelin, and conclusions are primarily based on MRI of formalin-fixed tissue.
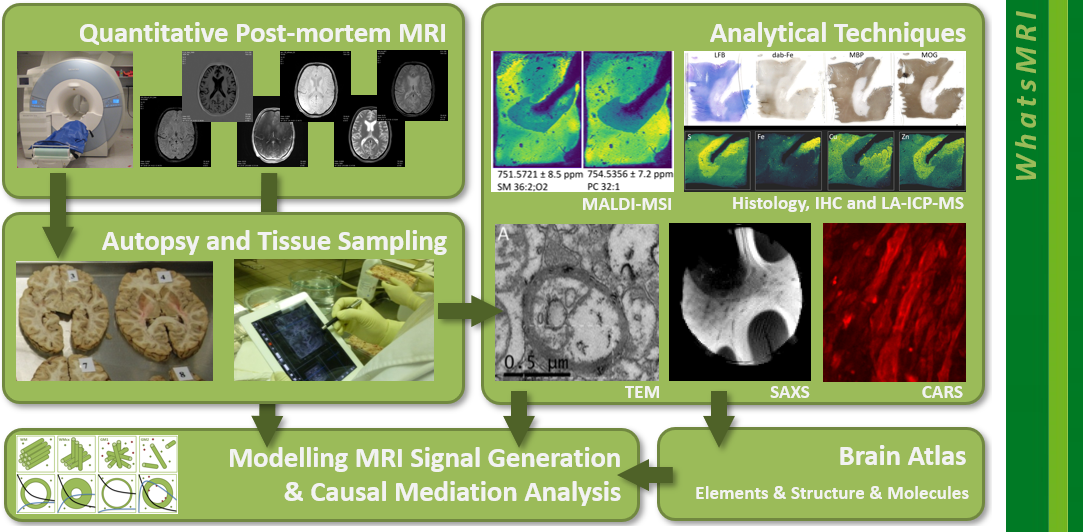
Quantitative post-mortem MRI of unfixed human brains in situ, combined with subsequent mass spectrometry imaging (LA-ICP-TOF-MS, MALDI-MSI), small-angle X-ray scattering (SAXS), and microscopy (CARS, TEM, IHC), will enable histologically enriched modelling of tissue and the simulation of fundamental MRI parameters (relaxometry, susceptibility, and diffusion) to reveal causal relationships with chemical elements, matrix composition, structure, and common molecules of myelin, neural fiber orientation, and biometals.
This research addresses the fundamental biophysical mechanisms underlying MRI of myelin and chemical elements, which currently lack validation. We will establish a publicly available elemental and histochemical atlas of the human brain and identify how histological features causally contribute to quantitative MRI parameters.
Graphical project portfolio
Jobs
We have multiple postdoc/PhD/MSc positions open in WhatsMRI starting Q3/2025. If you are enthusiastic about this project send an email to Christian.
Collaborators
DESY Hamburg, Stanford, Uni Münster, Uni Graz, TU Graz



